BY KEVIN COLLIER AND FRAN BERKMAN
Microsoft often charges the FBI’s most secretive division hundreds of thousands of dollars a month to legally view customer information, according to documents allegedly hacked by the Syrian Electronic Army.
The SEA, a hacker group loyal to Syrian President Bashar al-Assad, is best known for hijacking Western media companies’ social media accounts. (These companies include the Associated Press, CNN, NPR, and even the Daily Dot.) The SEA agreed to let the Daily Dot analyze the documents with experts before the group published them in full.
The documents consist of what appear to be invoices and emails between Microsoft’s Global Criminal Compliance team and the FBI’s Digital Intercept Technology Unit (DITU), and purport to show exactly how much money Microsoft charges DITU, in terms of compliance costs, when DITU provides warrants and court orders for customers’ data.
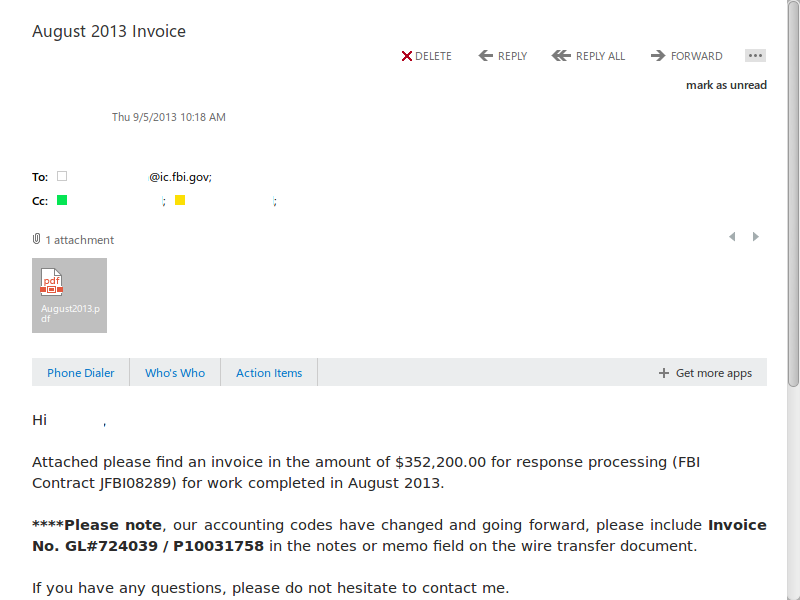
In December 2012, for instance, Microsoft emailed DITU a PDF invoice for $145,100, broken down to $100 per request for information, the documents appear to show. In August 2013, Microsoft allegedly emailed a similar invoice, this time for $352,200, at a rate of $200 per request. The latest invoice provided, from November 2013, is for $281,000.

None of the technologists or lawyers consulted for this story thought that Microsoft would be in the wrong to charge the FBI for compliance, especially considering it’s well within the company’s legal right to charge “reasonable expenses.” Instead, they said, the documents are more of an indication of just how frequently the government wants information on customers. Some of the DITU invoices show hundreds of requests per month.
For ACLU Principal Technologist Christopher Soghoian, the documents reiterated his stance that charging a small fee is a positive, in part because it creates more of a record of government tracking. In 2010, Soghoian actually chided Microsoft for not charging the Drug Enforcement Agency for turning over user records when instructed to by courts, noting that companies like Google and Yahoo did.
Nate Cardozo, a staff attorney for the Electronic Frontier Foundation, agreed, and told the Daily Dot the government should be transparent about how much it pays.
“Taxpayers should absolutely know how much money is going toward this,” he said.
Compared with the National Security Agency, which has seen many of its programs exposed by former systems analyst Edward Snowden, DITU has a low profile. But it runs in the same circles. Multiple law enforcement and technology industry representatives described DITU to Foreign Policy as the FBI’s liaison to the U.S.’s tech companies, and the agency’s equivalent to the NSA.
To that note, DITU is mentioned as a little-noticed detail from Snowden slides that detail the NSA’s notorious PRISM program, which allows it to collect users’ communications from nine American tech companies, including Microsoft. One slide explicitly mentions DITU’s role in getting data from those companies.
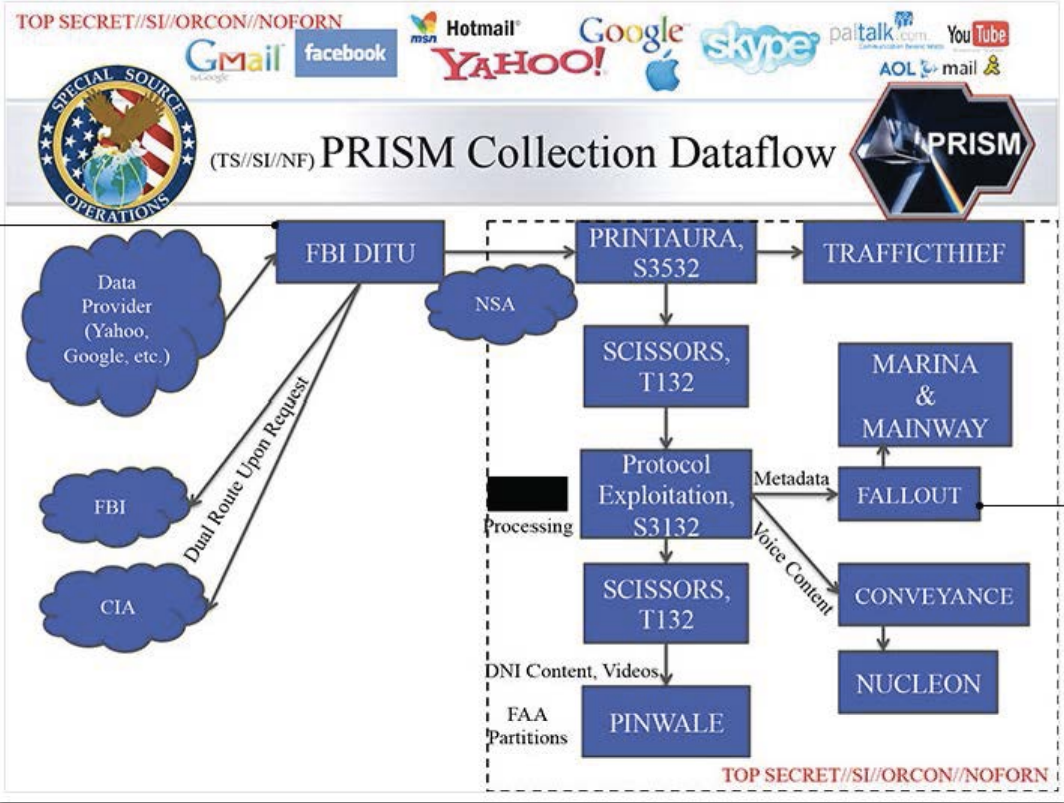
PRISM screengrab via freesnowden.is
It’s impossible to fully verify the documents’ authenticity without confirmation from someone with direct knowledge of Microsoft and DITU compliance practices, and those parties refused to comment. But there are multiple signs that indicate the documents are legitimate.
“I don’t see any indication that they’re not real,” Cardozo said. “If I was going to fake something like this, I would try to fake it up a lot more sensational than this.”
That the SEA twice attacked Microsoft with a phishing attack before leaking these documents is well documented. On Jan. 11, the day of the second attack, the SEA hijacked the company’s blog and Twitter account. One representative told the Verge that day that it was part of a bigger plan: “We are making some distraction for Microsoft employees so we can success in our main mission,” the hacker said.
In a blog post nearly two weeks later, Microsoft admitted: “[W]e have learned that there was unauthorized access to certain employee email accounts, and information contained in those accounts could be disclosed. It appears that documents associated with law enforcement inquiries were stolen.”
A source familiar with several of the email addresses of the Microsoft employees in the emails confirmed the addresses were authentic.
When reached for comment, the company reiterated its stance that it complies with government demands as required by law. A spokesperson added that “as pursuant to U.S. law, Microsoft is entitled to seek reimbursement for costs associated with compliance with a valid legal demands. … To be clear, these reimbursements cover only a portion of the costs we actually incur to comply with legal orders.”
A spokesperson for the FBI declined to comment and deferred questions to Microsoft, “given that SEA claims to have stolen the documents” from there.
Indeed, there’s plenty of history for communications companies charging compliance costs for cooperating with intelligence agencies’ request for people’s information. The CIA pays AT&T more than $10 million annually for access to its phone records, government officials told the New York Times. The Guardian, referencing other documents provided by Snowden, has reported that the NSA paid millions to Microsoft and the other eight companies used in PRISM for compliance costs.
Only the earliest of the Microsoft invoices provided by the SEA, dated May 10, 2012, breaks down requests by type of legal request, and it shows them to all explicitly come legally, though nothing in the documents indicates the later invoices refer to illegal surveillance. User information by a subpoena costs $50, a court order $75, and a search warrant $100. The requests come from FBI offices all around the U.S.

Later invoices to DITU don’t break down requests to subpoena and court order, though the format is otherwise similar, and costs begin to rise to $100 and $200 per request.
And though the costs vacillate slightly depending on the invoice, they appear to be roughly in line with industry standards. Ashkan Soltani, who coauthored a Yale study on how much it costs agencies like the FBI to track targets by tapping phone companies for their cellphone locations, said that the range of costs seen in the SEA documents—$50 to $200 per order to Microsoft—”did seem a fair cost.”
The invoices don’t make explicit the exact type of information Microsoft charges DITU to provide, which may account for the price changes.
The biggest suspicion espoused by the experts we spoke with was just how apparently easy it was for the SEA to acquire this sort of information. If the documents aren’t forged, that means Microsoft and the FBI simply email invoices and references to a presumably classified process.
“I’m surprised that they’re doing it by email,” Soltani said. “I thought it would be a more secure system.”
Illustration by Jason Reed