The road to accessibility for safe and legal abortions in the United States has been long, dark and exhausting, leading to constant opposition long after Roe v. Wade decriminalized abortion in 1973. On a federal level, it’s illegal to get an abortion in the U.S. “post-viability,” or after a fetus is considered capable of life outside the womb. But as long as Roe stands firm, states can override the constitution with their own regulations and abortion laws.
The Supreme Court’s decision to landmark Roe confirmed that abortion is a constitutional right and launched the fight for women’s reproductive rights. Anti-choice politicians and organizations have always worked to erode women’s rights until abortion is illegal altogether—but under an administration that prioritizes tax bills aimed at cutting basic healthcare for women and their families, pushes a pro-life agenda, and diminishes the right to choose, women’s bodies are even more trapped in the middle of a political tug-of-war.
Abortion laws by state in the U.S.
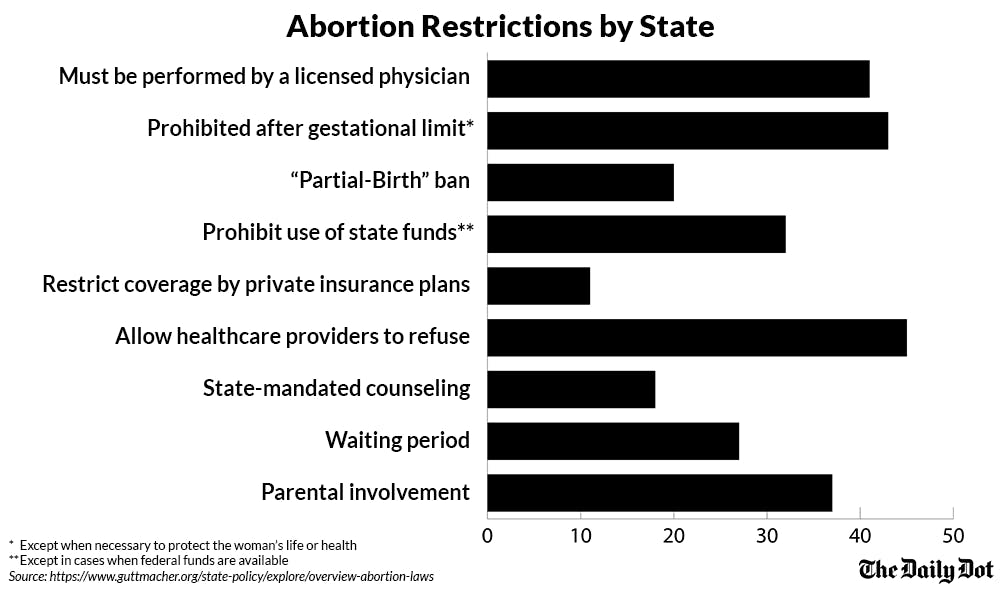
In 2017, 19 states adopted 63 new restrictions on abortion rights and access. The adoptions and enforced laws are the largest number of abortion restrictions legislated in the span of a year since 2013. In March 2018, Mississippi passed the most restrictive abortion law in the country, outlawing abortions after 15 weeks.
While the numbers are jarring, proactive efforts are still being exercised to expand the access to reproductive health and abortion. Last year alone, 21 states adopted 58 new proactive measures, which is 30 more than 2016. The new measures include 11 on topics like sex education, 12 on abortion access, and 35 on contraception.
Of the new restrictions passed, six states have adopted enough laws against abortion access to be considered hostile and 23 states are considered extremely hostile toward the topic. States have passed 401 abortion restrictions since 2011, which make up 34% of restrictions enacted since Roe was legalized, and continue to push further against abortion access for women.
In an effort to restrict access further, many states place unnecessary burdens on funding, propose “TRAP” (Targeted Regulation of Abortion Providers) laws that impose stricter requirements on abortion providers and facilities, and state budget cuts that defund Planned Parenthood. Nearly half of the country requires women to attend state-mandated counseling and wait, often up to three business days or longer, before the expensive procedure. Hurdles like these are intended to change a woman’s mind or covertly delay the procedure until it is no longer legal. Still, one study in Utah shows that a waiting period doesn’t decrease the number of women seeking an abortion, but instead costs the state more money.
Depending on where you live, your ability to access a safe abortion varies. In hopes of making a battleground feel less cluttered, here are all the current restrictions, gestational limitations, loopholes, and other abortion laws in all 50 states.
Alabama
Restrictions: Alabama outlaws abortion after 20 weeks since gestation unless it’s to save the patient’s life or in cases of rape or incest. The state also bans a D&E (dilation and evacuation) abortion, a commonly used method for second-trimester abortion, and post-viability abortion unless it’s to save the woman’s life.
Physician requirements: Only physicians licensed by the state to practice medicine or osteopathy can provide an abortion.
Mandatory counseling and waiting period: A woman seeking an abortion is required to attend biased counseling to discourage her from the procedure, and will be informed of the medical implications and the possible emotional and physical side effects. A woman seeking an abortion must wait for at least 48 hours after receiving the state-prepared documents and mandatory counseling before she can get the procedure.
Funding: The state prohibits public funding for women eligible for state medical assistance for general health care unless the woman’s life is in danger, rape, or incest.
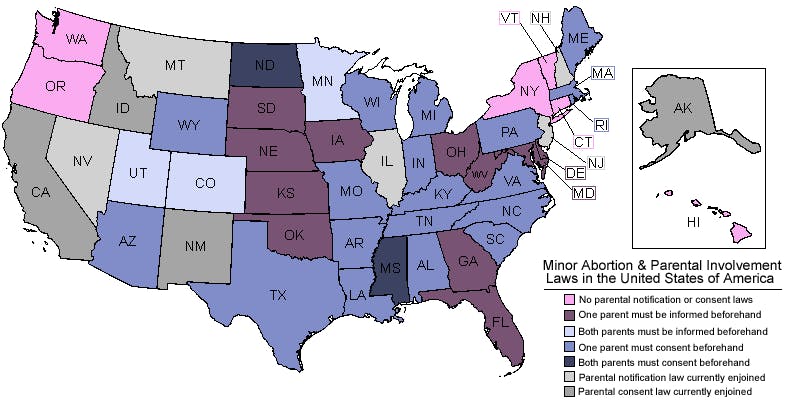
Parental consent: If a woman under the age of 18 seeks an abortion, at least one parent must consent to the procedure.
READ MORE:
- The financial costs of an uninsured abortion
- How does federal funding for Planned Parenthood actually work?
- Your birth control options, ranked from most effective to least
- The woman-led quest for the best condom on the market
Alaska
Restrictions: Alaska only allows certain individuals or entities, like hospitals or practices, to refuse to provide abortion services.
Physician requirements: All abortion services must be provided in a hospital, in a facility approved for that purpose by the state, or in a federal government hospital. Only a physician or surgeon licensed by the state can provide an abortion. A woman must also have an ultrasound before the procedure, and the abortion provider is required to ask if they want to see the picture of the unborn child.
Funding: A woman who qualifies for state medical assistance can receive public funds for an abortion only if her health is in danger of the pregnancy.
Mandatory counseling: A woman seeking an abortion is required to attend biased-counseling to discourage her from the procedure. The woman will also be given an option to watch a state-issued video about abortion.
Parental consent: If a woman under the age of 18 seeks an abortion, the physician must inform at least one parental guardian before the procedure.
Arizona
Restrictions: Arizona has a near-total abortion ban where it’s illegal after 20 weeks since gestation unless to save the mother’s life, or in the case of rape or incest. A safe second-trimester abortion is illegal, even if the mother’s life or health is at risk.
Physician requirements: Only physicians approved by the state are able to perform an abortion. Every abortion provider is required to perform an ultrasound on a woman seeking an abortion 24 hours before the procedure.
Funding: Arizona state public funds may not cover an abortion unless it is to save a woman’s life, or in the case of rape or incest. However, women on Medicaid will not receive coverage, even if it’s medically necessary.
Mandatory counseling and waiting period: Women are required to attend mandatory biased counseling that is intended to persuade her otherwise. After mandatory counseling, a woman seeking an abortion must wait at least 24 hours before getting the procedure done.
Parental consent: Any woman under the age of 18 has to have at least one parent or guardian provide consent.
Arkansas
Restrictions: Arkansas bans abortion procedure after 20 weeks since gestation, unless it’s to save the mothers life, or in the case of rape or incest. A common procedure D&E is banned.
Physician requirements: Only a physician licensed to practice medicine in the state may provide an abortion, and individuals and hospitals can refuse to provide the procedure. A woman is required to receive an abdominal ultrasound before the procedure to determine if the fetus has a heartbeat. If a heartbeat is detected, the procedure is prohibited.
Funding: State public funding and healthcare plans only cover abortions if it’s to save the mothers life, or in the case of incest or rape.
Mandatory counseling and waiting period: Women must receive biased counseling intended to persuade her otherwise. Women are also required to attend a state-mandated lecture by the providing physician about the abortion, along with the option to read state-prepared materials. After attending the biased counseling, a woman must wait at least 48 hours before the procedure.
California
Protections: California has extra protections on reproductive rights with the affirmative right to choose written in its state law.
Physician requirements: Anyone with a certified licensed by the state can perform an abortion.
Funding: There is no co-pay for contraceptives and women who qualify for state medical assistance can receive funds for an abortion.
Parental consent: Any woman under 18 years old is required to get parental consent before receiving an abortion.
Colorado
Funding: Colorado does not provide public funding for state employees or women eligible for medical assistance unless it’s in the case of rape, incest, or to save the mother’s life.
Parental consent: Any woman under 18 years old is required to get parental consent before receiving an abortion.
Connecticut
Protections: Connecticut implements protections on a woman’s right to an abortion with an affirmative right to choose in its state law. Victims of sexual assault are also able to receive immediate emergency contraception at a hospital if requested.
Restrictions: Abortion is banned after viability.
Physician requirements: Only state-certified physicians can perform an abortion, and it has to occur in a designated operating room.
Funding: There are no restrictions on funding, any woman who qualifies for state medical assistance may receive public funding for an abortion.

Delaware
Restrictions: Delaware has not repealed its pre-Roe vs. Wade abortion ban, so the state nearly bans it altogether. An abortion is banned after 20 weeks unless the case is reviewed by a hospital authority and finds the abortion is necessary in the case of rape incest, saving the mother’s life, or child deformation or retardation.
Physician requirements: Only physicians licensed by the state can perform an abortion.
Mandatory counseling and waiting period: The state has an unenforceable law that stating women must receive biased counseling and wait to 24 hours before getting an abortion.
Funding: Public funding is prohibited for women eligible for state medical assistance unless, in the case of rape, incest reported to the police, or to save the mother’s life.
Parental consent: Women under 16 are required to notify their parents at least 48 hours in advance of the procedure. It can be waived by a medical professional if necessary.
Florida
Restrictions: Florida bans an abortion after 24 weeks unless it’s in the case of rape, incest, or to save the woman’s life.
Physician requirements: Abortions are required to be performed in an abortion clinic licensed by the state. The woman is also required to undergo an ultrasound before the procedure, and the physician to offer the woman an opportunity to see a photo of the fetus.
Funding: The state prohibits public funding for women eligible for medical assistance unless its to save the woman’s life.
Parental notification: Women under the age of 18 must notify a parent of the procedure at least 24 hours before. The requirement can be waived by a physician unless it’s in the case of rape or incest.
Georgia
Restrictions: Georgia bans abortion after 20 weeks since gestation, unless the pregnancy is not viable, or to save the woman’s life.
Physician requirements: Only physicians licensed by the state can perform an abortion.
Biased counseling and waiting period: Women must receive biased counseling before an abortion, and then must wait 24 hours after counseling before receiving an abortion.
Funding: Funding for state employees is prohibited unless its to save the woman’s life. State public funding is prohibited as well unless it’s in the case of rape, incest, or to save the woman’s life.
Parental notice: Any woman under the age of 18 must notify at least one parent before the procedure.
Hawaii
Protections: Hawaii created extra protections for reproductive rights by adding the affirmative right to choose into its state law.
Physician requirements: Only a state-licensed physician can provide an abortion.
Funding: Women who are eligible for medical assistance can receive public funding.
Idaho
Restrictions: Idaho has an anti-choice law that bans abortion after 20 weeks since gestation unless its to save the mother’s life.
Physician requirements: Only a state-licensed physician can provide an abortion.
Biased counseling and waiting period: Women must receive biased counseling before the procedure, and then wait 24 hours after counseling before receiving an abortion.
Funding: Private insurers will only cover abortions if the mother’s life is in danger of the pregnancy. Abortion is also only covered by the insurance plan for public employees if their life is endangered. Public funding is prohibited unless in cases of life endangerment, rape, or incest.
Parental notice: Any woman under the age of 18 must notify at least one parent before the procedure.
Illinois
Protections: Illinois created extra protections for reproductive rights by adding the affirmative right to choose into its state law.
Physician requirements: Only physicians licensed to practice medicine may provide abortion care.
Parental notification: Any woman under the age of 18 must notify at least one parent before the procedure.
READ MORE:
- What is universal healthcare?
- 11 important things you didn’t know about Planned Parenthood
- When was birth control invented? A brief history of the pill
- The reason why IUDs are so popular right now
Indiana
Restrictions: Indiana bans abortion after 20 weeks since gestation, unless the woman’s life or health is in danger.
Physician requirements: Only a physician licensed to practice medicine in the state may provide an abortion. Women must have an ultrasound before the procedure, and the physician must offer the woman a chance to look at the image.
Biased counseling and waiting period: Women must receive biased counseling, and then wait 18 hours after being counseled before undergoing the procedure.
Funding: Abortions are only funded by private insurers and insurance plans for public employees in the case of life endangerment, rape, or incest. Public funding is prohibited except for cases of life endangerment, rape, or incest.
Parental consent: Any woman under the age of 18 must receive at least one parent’s consent before the procedure.
Iowa
Restrictions: An abortion may only be performed in the third trimester if the woman’s life or health is in danger.
Funding: Public funding for an abortion are available in the case of life endangerment, rape, or incest. Medicaid must be approved by the governor.
Parental notification: Any woman under the age of 18 must notify at least one parent before the procedure.
News: In 2018, the Iowa legislature fast-tracked a bill known as the “heartbeat” bill, which seeks to ban most abortions once a fetal heartbeat has been detected. The legislation is predicted to be challenged in court for violating Supreme Court rulings like Roe v. Wade.
Kansas
Restrictions: Kansas has an anti-choice law that bans abortion after 22 weeks since gestation unless it’s to save the mother’s life.
Requirements: Women must have an ultrasound before the procedure, and the physician must offer the woman a chance to look at the image.
Biased counseling and waiting period: Women are required to receive biased counseling, and then wait at least 24 hours after being counseled before an abortion.
Funding: Abortions are only funded by private insurers and insurance plans for public employees in the case of life endangerment, rape, or incest. Public funding is prohibited except for cases of life endangerment.
Parental consent: Any woman under the age of 18 must receive at least one parent’s consent before the procedure.

Kentucky
Restrictions: Kentucky bans abortion after 20 weeks since gestation unless it is to save the mothers life, or her health is in danger.
Biased counseling and waiting period: Women must receive biased counseling, and then wait 24 hours after being counseled before undergoing the procedure.
Funding: Abortions are only funded by private insurers in the case of life endangerment. Insurance plans for public employees do not cover abortions. Public funding is prohibited except for cases of life endangerment, rape, or incest.
Parental consent: Any woman under the age of 18 must receive at least one parent’s consent before the procedure.
Louisiana
Restrictions: Louisiana bans abortion after 20 weeks since gestation, or post-viability unless it is to save the mother’s life. If Roe v. Wade is overturned abortion will automatically become illegal in the state.
Biased counseling and waiting period: Women are required to receive biased counseling, and then wait at least 24 hours after being counseled before an abortion.
Funding: Public funding is only available in the case of life endangerment, rape, or incest.
Parental consent: Any woman under the age of 18 must receive at least one parent’s consent before the procedure.
Maine
Protections: Maine created extra protections for reproductive rights by adding the affirmative right to choose into its state law.
Physician requirements: Only physicians licensed to practice medicine may provide abortion care.
Funding: Public funding is available in the case of life endangerment, rape or, incest.
Maryland
Protections: Maryland created extra protections for reproductive rights by adding the affirmative right to choose into its state law.
Physician requirements: Only physicians licensed to practice medicine may provide abortion care.
Funding: Women eligible for state medical assistance can obtain public funds for an abortion.
Parental consent: Any woman under the age of 18 must receive at least one parent’s consent before the procedure.
Massachusetts
Protections: Massachusetts created extra protections for reproductive rights by adding the affirmative right to choose into its state law. However, the state bans an abortion after 24 weeks unless it’s to save the woman’s life or when her health is endangered.
Physician requirements: Only physicians licensed to practice medicine may provide abortion care.
Parental consent: Any woman under the age of 18 must receive at least one parent’s consent before the procedure.
Michigan
Restrictions: Michigan has not repealed its pre-Roe abortion ban, and the court has tried to ban abortion four times. An abortion is banned post-viability unless it is to save the woman’s life.
Biased counseling and waiting period: Women must receive biased counseling, and then wait 24 hours after being counseled before undergoing the procedure.
Funding: Abortions are only funded by private insurers and insurance plans for public employees in the case of life endangerment. Public funding is prohibited except for cases of life endangerment, rape, or incest.
Parental consent: Any woman under the age of 18 must receive at least one parent’s consent before the procedure.
Minnesota
Protections: Minnesota created extra protections for reproductive rights by adding the affirmative right to choose into its state law.
Biased counseling and waiting period: Women must receive biased counseling, and then wait 24 hours after being counseled before undergoing the procedure.
Parental notification: Any woman under the age of 18 must notify at least one parent before the procedure.
Mississippi
Restrictions: Mississippi bans abortion after 20 weeks since gestation without adequate exceptions, though a 2018 bill outlawing abortion after 15 weeks could be signed into law. for If Roe v. Wade is overturned abortion will automatically become illegal in the state.
Requirements: Women must have an ultrasound before the procedure, and the physician must offer the woman a chance to look at the image.
Biased counseling and waiting period: Women must receive biased counseling, and then wait 24 hours after being counseled before undergoing the procedure.
Funding: Abortions are only funded by private insurers and insurance plans for public employees in the case of life endangerment, rape, or incest.
Parental consent: Any woman under the age of 18 must receive at least one parent’s consent before the procedure.
Missouri
Restrictions: Missouri bans a safe abortion. Abortion is not legal at or post-viability unless it’s to save the woman’s life or preserve her health.
Biased counseling and waiting period: Women must receive biased counseling, and then wait 72 hours after being counseled before undergoing the procedure.
Funding: Abortions are only funded by private insurers and insurance plans for public employees in the case of life endangerment, rape, or incest. Public funding is the same.
Parental consent: Any woman under the age of 18 must receive at least one parent’s consent before the procedure.
Montana
Protections: Montana created extra protections for reproductive rights by adding the affirmative right to choose into its state law. However, an abortion is only legal at or post-viability if it’s to save the woman’s life or preserve her health.
Funding: Public funding is available in the case of life endangerment, rape, or incest.
Nebraska
Restrictions: Nebraska has an anti-choice law that bans abortion after 20 weeks since gestation unless it’s to save the woman’s life.
Biased counseling and waiting period: Women must receive biased counseling, and then wait 24 hours after being counseled before undergoing the procedure.
Funding: Abortions are only funded by private insurers and insurance plans for public employees in the case of life endangerment. Public funding is only available in the case of life endangerment, rape, or incest.
Parental consent: Any woman under the age of 18 must receive at least one parent’s consent before the procedure.
Nevada
Restrictions: Nevada bans abortion after 24 weeks since gestation unless it’s to save the woman’s life or preserve her health.
Funding: Public funding is only available in the case of life endangerment, rape, or incest.
New Hampshire
Restrictions: New Hampshire bans a safe second-trimester abortion with no adequate exceptions to the woman’s health.
Parental notification: Any woman under the age of 18 must notify at least one parent before the procedure.
Funding: Public funding is only available in the case of life endangerment, rape, or incest.
READ MORE:
- The best political podcasts to keep you informed
- The varying age of consent from state to state
- What is socialism, really?
- Who’s going to challenge Trump in 2020? Here are the super-early contenders
New Jersey
Protections: New Jersey created extra protections for reproductive rights by adding the affirmative right to choose into its state law.
Funding: Public funding is available for women eligible for state medical assistance.
New Mexico
Protections: New Mexico created extra protections for reproductive rights by adding the affirmative right to choose into its state law.
Funding: Public funding is available for women eligible for state medical assistance.
New York
Restrictions: New York bans abortion after 24 weeks since gestation unless its to save the woman’s life or preserve her health.
North Carolina
Restrictions: Mississippi bans abortion after 20 weeks since gestation unless it’s to save the woman’s life or preserve her health.
Physician requirements: Only physicians licensed by the state can provide an abortion. Women must have an ultrasound before the procedure, and the physician must offer the woman a chance to look at the image.
Biased counseling and waiting period: Women must receive biased counseling, and then wait 72 hours after being counseled before undergoing the procedure.
Funding: Abortions are only funded by private insurers and insurance plans for public employees in the case of life endangerment, rape, or incest. Public funding is the same.
Parental consent: Any woman under the age of 18 must receive at least one parent’s consent before the procedure.
North Dakota
Restrictions: North Dakota has an anti-choice law that bans abortion after 20 weeks since gestation unless its to save the woman’s life or preserve her health. If Roe v. Wade is overturned abortion will automatically become illegal in the state. The FDA must also approve abortion medication taken under its protocol.
Biased counseling and waiting period: Women must receive biased counseling, and then wait 24 hours after being counseled before undergoing the procedure.
Funding: Abortions are only funded by private insurers and insurance plans for public employees in the case of life endangerment. Public funding is only available in the case of life endangerment, rape, or incest.
Parental consent: Any woman under the age of 18 must receive at least one parent’s consent before the procedure.
Ohio
Restrictions: Ohio bans abortion post-viability unless it is to save the woman’s life or if her health is severely in danger. The FDA must also approve abortion medication taken under its protocol.
Requirements: Women must have an ultrasound before the procedure, and the physician must offer the woman a chance to look at the image.
Biased counseling and waiting period: Women must receive biased counseling, and then wait 24 hours after being counseled before undergoing the procedure.
Funding: Abortions are only funded by private insurers and insurance plans for public employees in the case of life endangerment, rape, or incest. Public funding is the same.
Parental consent: Any woman under the age of 18 must receive at least one parent’s consent before the procedure.

Oklahoma
Restrictions: Oklahoma has an anti-choice law that bans abortion after 20 weeks since gestation unless its to save the woman’s life or her health is compromised.
Biased counseling and waiting period: Women must receive biased counseling, and then wait 24 hours after being counseled before undergoing the procedure.
Funding: Abortions are only funded by private insurers and insurance plans for public employees in the case of life endangerment. Public funding is only available in the case of life endangerment, rape, or incest.
Parental consent: Any woman under the age of 18 must receive at least one parent’s consent before the procedure.
Oregon
Protections: Oregon created extra protections for reproductive rights by adding the affirmative right to choose into its state law.
Funding: Public funding is available for women eligible for state medical assistance.
Pennsylvania
Restrictions: Pennsylvania has an anti-choice law that bans abortion after 24 weeks since gestation unless its to save the woman’s life or her health is compromised.
Biased counseling and waiting period: Women must receive biased counseling, and then wait 24 hours after being counseled before undergoing the procedure.
Funding: Abortions are only funded by private insurers and insurance plans for public employees in the case of life endangerment, rape, or incest. Public funding is the same.
Parental consent: Any woman under the age of 18 must receive at least one parent’s consent before the procedure.
Rhode Island
Restrictions: Rhode Island prohibits abortion after viability or when the fetus’s heart is beating unless it’s to save the mother’s life.
Physician requirements: Only physicians licensed by the state can provide an abortion.
Biased counseling: A woman seeking an abortion must receive biased counseling where a physician informs her of the fetus’s age and nature of the procedure.
Funding: The state prohibits public funding for women seeking an abortion unless it’s int he case of rape, incest, or to save her life.
Parental consent: A woman under the age of 18 seeking an abortion must have at least one parent’s consent.
South Carolina
Restrictions: South Carolina bans abortion after 24 weeks since gestation unless the attending physician writes it is necessary to save the mother’s life. Abortion clinics are also subject to more than 30 pages of regulations that restrict administration, professional qualifications, location and more.
Biased counseling and waiting period: Women are required to receive biased counseling, and then wait at least 24 hours after counseling before an abortion.
Funding: The state prohibits public funding for women eligible for medical assistance unless it’s in the case of rape, incest, or to save the mother’s life.
South Dakota
Restrictions: South Dakota has an anti-choice law banning abortion 24 weeks after gestation unless it’s to save the mother’s life.
Physician requirements: Only a physician licensed by the state can provide an abortion.
Biased counseling and waiting period: A woman seeking an abortion must receive biased counseling before the procedure, and must wait at least three business days after counseling to receive an abortion.
Funding: The state prohibits public funding unless it’s to save the woman’s life.
Parental notice: A woman under the age of 18 and not emancipated must notify at least one parent before the procedure.
Tennessee
Restrictions: Tennessee bans abortion after viability unless it’s necessary to save the mother’s life.
Physician requirements: Only physicians licensed by the state can provide an abortion.
Biased counseling and waiting period: A woman seeking an abortion must receive biased counseling before the procedure, and then must wait at least 48 hours before receiving an abortion.
Funding: Public funding is only available in the case of rape, incest, or to save the mother’s life.
Texas
Restrictions: Texas bans abortion 20 weeks after gestation unless it’s to save the mother’s life or in the case of a severe fetal anomaly. An abortion may also only be provided in a licensed abortion clinic. Telemedicine and D&E procedures are banned.
Physician requirements: Only a physician licensed by the state may provide an abortion.
Biased Counseling and waiting period: A woman seeking an abortion must receive biased counseling, and then must wait 24 hours after before receiving an abortion.
Funding: The state prohibits public funding unless the abortion is required to save the mothers life, or it’s in the case of rape or incest.
Parental consent: A woman under 18 seeking an abortion must notify and receive consent from at least one parent unless she is married.

Utah
Restrictions: Abortion providers must be located within 15 or less from a full-service hospital, and need to have a proper license. The state prohibits an abortion after viability unless it’s to save the mother’s life, prevent a defective birth, or in the case of rape or incest reported to the police. The state also bans a safe abortion without the exception of preserving the mother’s health.
Physician requirements: Only physicians licensed by the state can perform an abortion.
Biased counseling and waiting period: A woman seeking an abortion must receive biased counseling in person, and must wait 72 hours after counseling before receiving an abortion.
Funding: The state prohibits public funding for an abortion unless it’s in the case of rape, incest, or to save the mother’s life.
Vermont
Protections: The state’s constitution protects the right to choose to a greater extent than the U.S. Constitution.
Funding: Women eligible for medical assistance for general health care are able to receive public funds.
Virginia
Restrictions: Abortions are banned after post-viability in the second trimester unless the attending physician and two others approve the procedure is needed to save the mother’s life.
Third-trimester abortion: A third-trimester abortion may be performed only if it’s in the case of saving the mother’s life.
Physician requirements: Only physicians licensed by the state can provide an abortion. A woman must also receive an ultrasound at least 24 hours before an abortion, and the provider must offer the mother an opportunity to look at the photo.
Biased counseling and waiting period: A woman seeking an abortion must receive biased counseling at least 24 hours before an abortion procedure. The woman then must wait another 24 hours until receiving an abortion.
Funding: Women eligible for medical assistance are not allowed to receive public funding unless it’s to save the mother’s life, or in the case of rape or incest reported to the police. State employees with benefits from the Commonwealth of Virginia Health Benefits Plan may not receive coverage unless it’s with the same exceptions.
Parental consent: Any woman under the age of 18 must have at least one parent’s consent.
Washington
Restrictions: Washington allows certain individuals or private medical facilities to refuse abortion services.
Physician requirements: Only physicians licensed by the state can provide an abortion.
Funding: The state allows women eligible for medical assistance for maternity-care benefits to obtain public funds for an abortion.
Washington, D.C.
Protections: Washington, D.C. created extra protections for reproductive rights by adding the affirmative right to choose into its state law.
Funding: Women eligible for medical assistance may not receive public funding for an abortion unless it’s medically necessary to save the mother’s life.
West Virginia
Restrictions: West Virginia bans abortion after 20 weeks since gestation with no exception of rape, incest, or to save the mother’s life. The state also outlaws a D&E procedure.
Biased counseling and waiting period: A woman seeking an abortion must receive biased counseling and a state-mandated lecture by a physician at least 24 hours before an abortion. The woman then has to wait another 24 hours after counseling before receiving an abortion.
Funding: Women eligible for medical assistance may receive public funding for an abortion if it’s medically necessary, to save the mother’s life, or in the case of rape or incest.
Parental notice: A woman seeking an abortion must notify at least one parent.

Wisconsin
Restrictions: Wisconsin bans abortion 20 weeks since gestation with no exception of rape, incest, or to save the mother’s life.
Physician requirements: Physicians may only provide first-trimester abortion services within 30 minutes of traveling time to the hospital. No exceptions are made for rural areas.
Counseling and waiting period: A woman seeking an abortion must attend biased counseling 24 hours prior to an abortion, as well as a state-mandated lecture. The woman then has to wait 24 hours after counseling to receive an abortion.
Funding: The state prohibits public funding for women eligible for medical assistance unless the pregnancy is a result of rape, incest, or to save the mother’s life.
Parental consent: Any minor eligible for an abortion must receive at least one parent’s consent.
Wyoming
Restrictions: Abortion is banned after viability unless it’s to save the mother from “imminent peril” that puts her life at risk.
Physician requirements: Only a physician licensed by the state can perform an abortion.
Funding: The state prohibits public funding for women eligible for medical assistance unless its to protect the mother’s life, the pregnancy is a result of incest or sexual assault and it’s reported to the police five days prior.
Parental consent: Any minor eligible for an abortion must notify both parents and get their consent.
Editor’s note: This article will be regularly updated according to relevance.